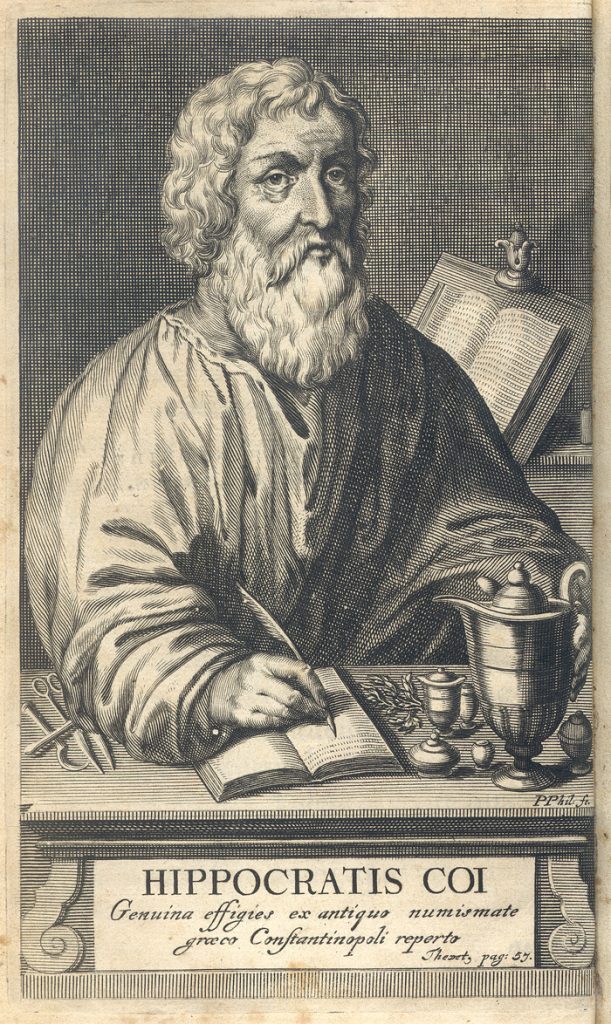
Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (c. 460 – c. 370 BC), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the Age of Pericles (Classical Greece), who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is often referred to as the “Father of Medicine”, in recognition of his lasting contributions to the field as the founder of the Hippocratic School of Medicine. This intellectual school revolutionized Ancient Greek medicine, establishing it as a discipline distinct from other fields with which it had traditionally been associated (theurgy and philosophy), thus establishing medicine as a profession. Hippocrates is credited with being the first person to believe that diseases were caused naturally, not because of superstition and gods. Hippocrates was credited by the disciples of Pythagoras of allying philosophy and medicine. He separated the discipline of medicine from religion, believing and arguing that disease was not a punishment inflicted by the gods but rather the product of environmental factors, diet, and living habits.

Hippocratic medicine was notable for its strict professionalism, discipline, and rigorous practice. The Hippocratic work on the physician recommends that physicians always be well-kempt, honest, calm, understanding, and serious. Besides the Hippocratic Oath, a seminal document on the ethics of medical practice, was attributed to Hippocrates in antiquity.